Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a common skin condition that affects up to 20% of the population at some point in their lives. Urticaria is characterized by red, itchy welts on the skin that can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The welts are usually raised, with a flat or slightly elevated center and a red, swollen border.
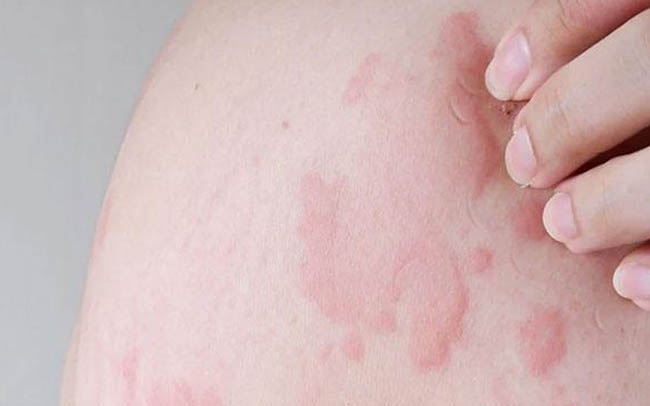
Urticaria can be acute or chronic. Acute urticaria typically lasts for less than 6 weeks, while chronic urticaria lasts for more than 6 weeks. Acute urticaria is usually caused by an allergic reaction to a substance, such as food, medication, or insect bites, while chronic urticaria may have multiple causes, including autoimmune disorders and underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms of Urticaria:
The symptoms of urticaria can vary in severity and duration, but typically include:
- Red, itchy welts on the skin
- Swelling of the affected area
- A burning or stinging sensation
- Blistering of the skin in severe cases
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing in rare cases
The welts can appear anywhere on the body and may move from one location to another over the course of a few hours. In some cases, the welts may merge to form larger, more extensive areas of swelling and redness.







