Ringworm/Fungal
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis or tinea, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. Despite its name, it is not caused by a worm, but by a group of fungi called dermatophytes that thrive in warm, moist environments. Ringworm can affect anyone, but it is more common in children and people who play contact sports or have close contact with infected animals.
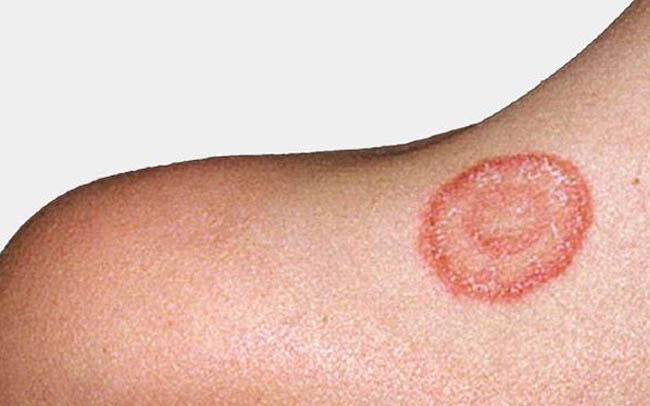
Causes of Ringworm
Ringworm is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can infect the skin, hair, and nails. Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread from person to person or from animal to person.
The most common ways of getting ringworm include:
Direct contact: Ringworm can spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal. This can happen when you touch an infected area on someone's skin, scalp, or nails, or when you come into contact with an infected animal's fur or skin.
Indirect contact: Ringworm can also spread through indirect contact. This can happen when you touch an object that has been contaminated with the fungus, such as a towel, a piece of clothing, or a hairbrush.
Pets: Some animals, such as dogs and cats, can also carry the fungus that causes ringworm. If you come into contact with an infected animal, you may develop ringworm.







